Hyundai Venue: Button Engine Start System / Description and operation
Hyundai Venue (QX) (2020-2025) Service Manual / Body Electrical System / Button Engine Start System / Description and operation
| Description |
System Overview
The System offers the following features:
| – |
Human machine interface through a 1-stage button, for terminal switching
and engine start.
|
| – |
Control of external relays for ACC / IGN1 / IGN2 terminal switching
and STARTER, without use of mechanical ignition switch.
|
| – |
Steering column locking with an ESCL device; Monitoring of the vehicle
status to insure safe activation of the ESCL.
|
| – |
Indication of vehicle status through LED or explicit messages on display.
|
| – |
Immobilizer function by LF transponder communication between fob and
start/stop button.
|
| – |
Redundant architecture for high system dependability .
|
| – |
Interface with Low Speed CAN vehicle communication network.
|
| – |
Interface with LIN vehicle communication network depending on platform
.
|
The RKE and SMART KEY functions are not considered part of this Button Engine
Start system and are specified in separated system.
System Main Function
| – |
Steering column locking/unlocking with ESCL.
|
| – |
Switching of ACC / IGN1 / IGN2 terminals.
|
| – |
Control of the STARTER relay BAT line (high side) based on communication
with EMS ECU.
|
| – |
Management of the Immobilizer function.
|
| – |
Management of BES warning function.
|
Button Engine Start System
The Button Start System allows the driver to operate the vehicle by simply pressing
a button (called as SSB) instead of using a standard mechanical key. It also
manages the locking and the unlocking of the steering column (called as ESCL)without
any specific actions by the driver.
If the driver press the SSB while prerequisites on brakes, fob authentication
and transmission status are satisfied, the BES System will proceed with the
locking/unlocking of the steering column, the control of the terminal, and the
cranking of the engine.
The driver can release the SSB as soon as this sequence initiated. After positive
response from immobilizer interrogation, the system will activate the starter
motor and communicate with the EMS to check the engine running status for starter
release.
The driver will be able to stop the engine by a short push on the SSB if the
vehicle is already in standstill. Emergency engine stop will be possible by
a long press of the SSB or 3 consecutive presses in case the vehicle is in ENGINE
RUNNING.
If the conditions for engine cranking are not satisfied while a push on the
SSB is detected and a valid fob authenticated, the system will unlock the steering
column and switch the terminals to IGN. Another push on the SSB will be necessary
to start the engine.
In case of a vehicle equipped with SMART KEY system, fob authentication will
not require any action from the driver. For limp home start or in case of vehicle
without SMART KEY, the driver will have to push the start / stop button.
| • |
Control Ignition and engine ON/OFF by Sending signal to IPM.
|
| • |
Display status by LED Lamp ON/OFF. (Amber or Blue)
|
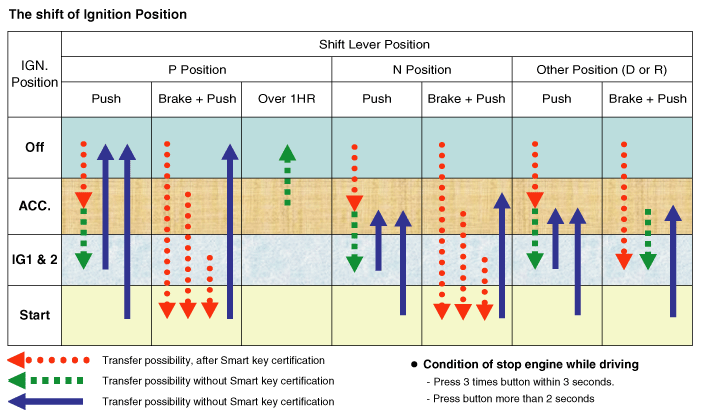
Indicator ON/OFF Condition at Ignition Key Off Condition
|
No |
Character lamp |
Conditions |
|
1 |
Indicator Lamp ON |
Door open, Tail lamp ON, ACC, IG ON |
|
2 |
Indicator Lamp 30sec ON → Lamp OFF |
Door close, Tail lamp OFF, IG OFF |
|
3 |
Indicator Lamp OFF |
Remote LOCK, Passive LOCK |
|
4 |
Rheostat at tail lamp ON (Illumination lamp) |
|
Indicator ON/OFF Condition According to Ignition Key's Position
|
No |
Ignition conditions |
Start Button LED status |
|
1 |
IG OFF |
LED OFF |
|
2 |
IG ACC |
Amber color LED ON |
|
3 |
IG ON (Engine OFF) |
Blue color LED ON |
|
4 |
Cranking |
Maintain LED status before cranking |
|
5 |
Engine running |
LED OFF |
Wireless Communication
Electromagnetic waves are used to exchange information between the vehicle and
the FOB. Two types of RKE Key can supplement the BES system:
| – |
Non-smart key RKE
|
| – |
SMART KEY FOB
|
Currently the BES system comprises with SMART KEY FOB always.
The transmitter, receiver and antennas required for the communication between
the fob and the vehicle will differ depending on functionalities and regional
areas.
The RKE and SMART KEY functions are in separated documents. Refer to Smart key
system for more detailed information about SMART KEY function.
Smart Key
The IBU manages all function related to:
| • |
"Start Stop Button (SSB) monitoring",
|
| • |
"Immobilizer communication" (with Engine Management System unit for
immobilizer release),
|
| • |
"ESCL control",
|
| • |
"Authentication server" (Validity of Transponder and in case of Smart
Key option Passive Fob authentication ),
|
| • |
"System consistency monitoring",
|
| • |
"System diagnosis",
|
| • |
Control of display message / warning buzzer .
|
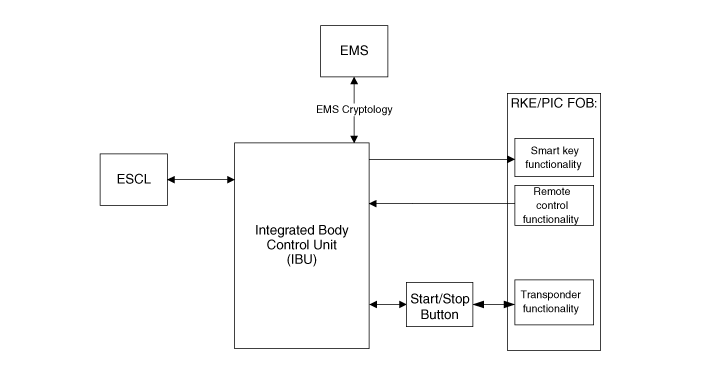
The unit behaves as Master role in the whole system.
In case of SMART KEY application, for example “Passive Access”, “Passive Locking”
and “Passive Authorization are integrated for ESCL/Terminal switching Operations”.
It collects information about vehicle status from other modules (vehicle speed,
alarm status, driver door open...), read the inputs (e.g. SSB, Lock Button and
PARK position Switch), controls the outputs (e.g. exterior and interior antennas),
and communicates with others devices via the CAN network as well as a single
line interfaces.
The diagnosis and learning of the components of the BES System are also handled
by the SMK.
Transponder
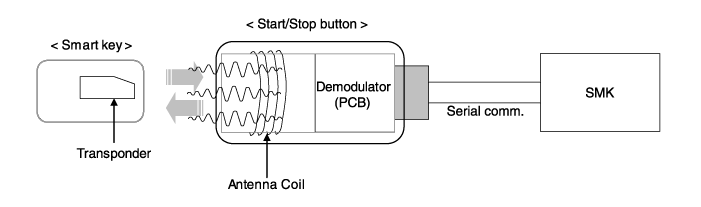
IBU (Intergrated Bocy Control Unit)
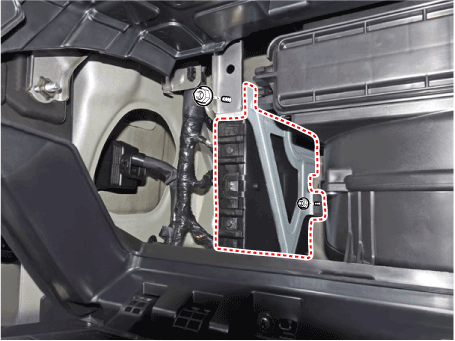
The IBU manages all function related to :
| • |
"Start Stop Button (SSB) monitoring",
|
| • |
"Immobilizer communication" (with Engine Management System unit for
immobilizer release),
|
| • |
"Authentication server" (Validity of Transponder and in case of Smart
Key option Passive Fob authentication ),
|
| • |
"System consistency monitoring",
|
| • |
"System diagnosis",
|
| • |
Control of display message / warning buzzer.
|
The unit behaves as Master role in the whole system.
In case of SMART KEY application, for example "Passive Access”, "Passive Locking”
and "Passive Authorization are integrated for Terminal switching Operations”.
It collects information about vehicle status from other modules (vehicle speed,
alarm status, driver door open...), reads the inputs (e.g. SSB, Capacitive Sensor
/ Lock Button, PARK position Switch), controls the outputs (e.g. exterior and
interior antennas), and communicates with others devices via the CAN network
as well as a single line interfaces.
The diagnosis and learning of the components of the BES System are also handled
by the IBU.
The IBU manages the functions related to the "terminal control" by activating
external relays for ACC, IGN1 and IGN2. This unit is also responsible for the
control of the STARTER relay.
The IBU is also controlling the illumination of the SSB as well as the "system
status indicator", which consists of 2 LEDs of different color. The illumination
of the fob holder is also managed by the SMK.
The IBU reads the inputs (Engine fob in, vehicle speed, relays contact status),
controls the outputs (Engine relay output drivers), and communicates with others
devices via the CAN.
The internal architecture of the IBU is defined in a way that the control of
the terminal is secured even in case of failure of one of the two microcontrollers,
system inconsistency or interruption of communication on the CAN network.
In case, failure of one of the two controllers, the remaining controller shall
disable the starter relay. The IGN1 and IGN2 terminals relays shall be maintained
in the state memorized before the failure and the driver shall be able to switch
those IGN terminals off by pressing the SSB with EMERGENCY_STOP pressing sequence.
However, engine restart will not be allowed. The state of the ACC relay will
depend on the type of failure.
The main functions of the IBU are :
| • |
Control of Terminal relays
|
| • |
Monitoring of the Vehicle speed received from sensor or ABS/ESP ECU.
|
| • |
Control of SSB LEDs (illumination, clamp state).
|
| • |
Control of the base station located in SSB through direct serial interface.
|
| • |
System consistency monitoring to diagnose SMK failure and to switch
to relevant limp home mode.
|
| • |
Providing vehicle speed information
|
| • |
Start Stop Button (SSB) monitoring
|
| • |
Starter power control
|
Start/Stop Button (SSB)
A single stage push button is used for the driver to operate the vehicle. Pressing
this button allows:
| • |
To activate the power modes ‘Off’, ’Accessory’, ‘Ignition’ and 'Start'
by switching the corresponding terminals
|
| • |
To start the engine
|
| • |
To stop the engine
|
The contact will be insured by a micro-switch and a backlighting is provided
to highlight the marking of the button whenever necessary.
Two (2) LED colors are located in the center of the button to display of the
status of the system. Another illumination LED is also integrated into the SSB
for the lighting of the "Engine Start/Stop" characters.

Electronic Steering Column Lock (ESCL)
The ESCL is needed to lock the steering column in order to prevent unauthorized
usage of the vehicle. In order to achieve the required safety integrity level,
the ESCL is controlled and monitored by the SMK. Such redundant architecture
guarantees that the ESCL motor is supplied only during locking/unlocking operation
and that it is disconnected from the battery and ground lines otherwise to avoid
unexpected operation while the vehicle is in motion.
Data are exchanged between the ESCL and SMK through an encrypted serial communication
interface.
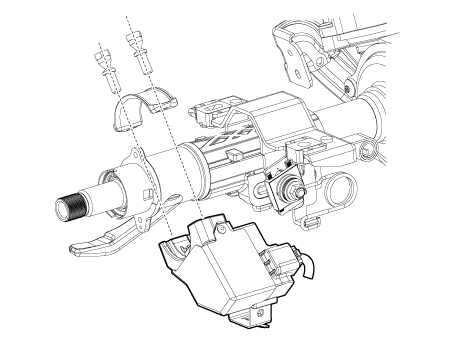
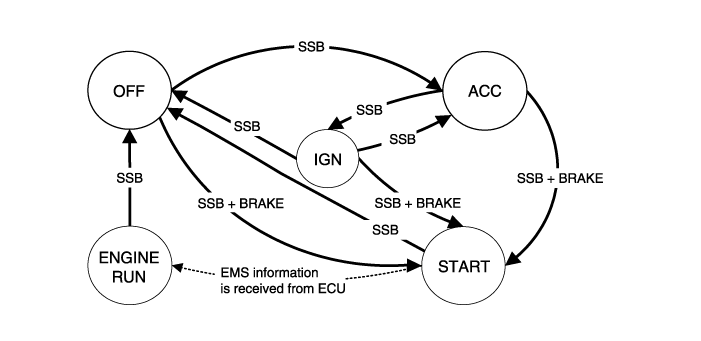
BES System State Chart
System States in Learnt Mode
In learnt mode, the BES System can be set in 6 different sates, depending on
the status of the terminals, ESCL and Engine status:
|
System State |
Terminal Status |
ESCL Status |
Engine Status |
|
1. OFF - Locked |
OFF |
Locked |
Stopped |
|
2. OFF - Unlocked |
OFF |
Unlocked |
Stopped |
|
3. ACC |
ACC |
Unlocked |
Stopped |
|
4. IGN |
IGN1, IGN2, ACC |
Unlocked |
Stopped |
|
5. Start |
IGN1, Start |
Unlocked |
Cranking |
|
6. IGN - Engine |
IGN1, IGN2, ACC |
Unlocked |
Running (means "self-running") |
Referring to the terminals, the system states described in the table above are
same as those one found in a system based on a mechanical ignition switch. The
one of distinction with Mechanical-Ignition-Switch based system is that the
BES system allows specific transition from [OFF] to [START] without going through
[ACC] and [IGN] states.
System States in Virgin Mode
The BES System can be set in 5 different states (OFF LOCKED is not available
in virgin mode), depending on the status of the terminals, ESCL and Engine status:
|
System State |
Terminal Status |
ESCL Status |
Engine Status |
|
1. OFF - UNLOCKED |
OFF |
Unlocked |
Stopped |
|
2. ACC |
ACC |
Unlocked |
Stopped |
|
3. IGN |
IGN1, IGN2, ACC |
Unlocked |
Stopped |
|
4. Start |
IGN1, START with special pattern of activation see Chap 6.2.1 for details |
Unlocked |
Cranking |
|
5. IGN - Engine |
IGN1, IGN2, ACC |
Unlocked |
Running (means "self-running") |
Referring to the terminals, the system states described in the table above are
same as those one found in a system based on a mechanical ignition switch. The
one of distinction with Mechanical-Ignition-Switch based system is that the
BES system allows specific transition from [OFF] to [START] without going through
[ACC] and [IGN] states.
Other information:
Hyundai Venue (QX) (2020-2025) Service Manual: Fuel Pump Motor. Repair procedures
Removal 1. Remove the fuel pump. (Refer to Fuel Delivery System - "Fuel Pump") 2. Disconnect the electric pump wiring connector (A) and the fuel sender connector (B)...
Hyundai Venue (QX) (2020-2025) Service Manual: Roof Side Molding. Repair procedures
Replacement • Put on gloves to prevent hand injuries. • When removing with a flat-tip screwdriver or remover, wrap protective tape around the tools to prevent damage to components...
Categories
- Manuals Home
- 1st Generation Venue Owners Manual
- 1st Generation Venue Service Manual
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
- To set Cruise Control speed
- Immobilizer System
- New on site
- Most important about car
Vehicle Identification Number (vin), Vehicle Certification Label
Vehicle Identification Number (vin)
Frame number
Copyright © 2025 www.hvenueqx.com


